crazyflies-Package
Crazyflie and Safeflie Classes
If you want to start scripting your own application logic, you can use the crazyflies package to create a Crazyflie or Safeflie.
The Crazyflie and Safeflie classes are examples of how to use the underlying interface to control a Crazyflie, they use the crazyflie interfaces package to do so. It is the easiest way to start implementing your own logic. A Crazyflie/Safeflie will automatically call the gateway to establish a Crazyflie connection.
If reduced functionality is required, it is recommended to use the Client classes to implement only parts of the communication on the application layer. This is especially important when using many Crazyflies to limit the number of ROS Topic connections.
The following class diagram shows the Crazyflie and Safeflie classes and how the user can interact with them.
Note
The ds-crazyflies repository tries to provide a universal framework for crazyflies. For a more detailed but therefore also more use-case specific example on how to use ds-crazyflies also check out the Pad Swarming repository. The repository allows to fly up to 50 Crazyflies equipped with QI-Charges.
Safeflie
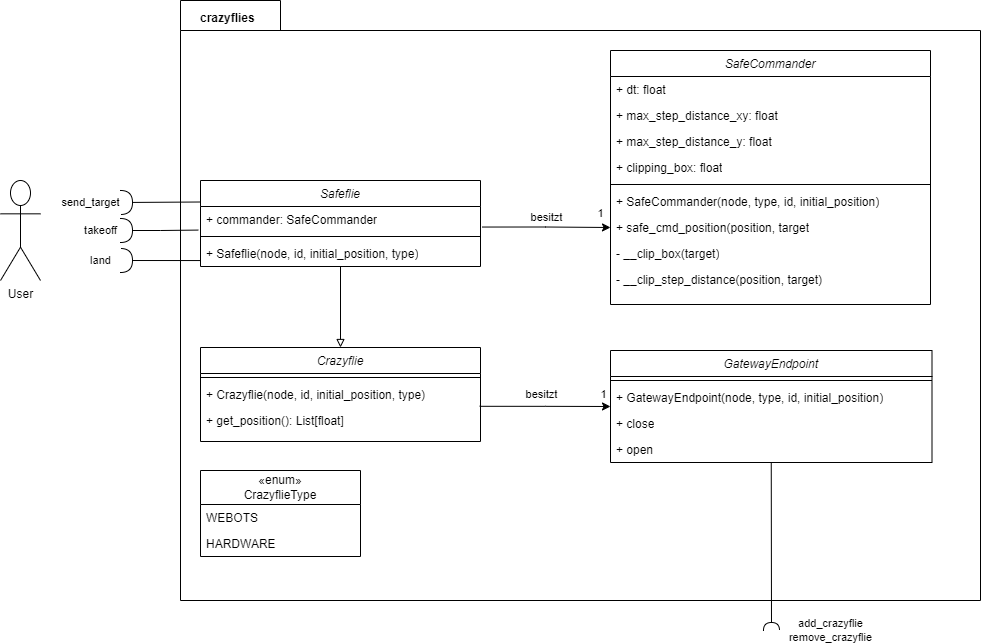
Note
Not shown in the diagram are the connections of the Crazyflie with the underlying software stack.
Crazyflie class
- class crazyflies.crazyflie.Crazyflie(node, id, channel, initial_position, type, tracked=False)
Bases:
ConsoleClient,EmergencyClient,GenericCommanderClient,HighLevelCommanderClient,LoggingClient,RPYTCommanderClientRepresents a crazyflie.
Allows user to interchangeably use different crazyflie implementations (currently Webots or Real Hardware)
- Parameters:
node (rclpy.node.Node)
id (int)
channel (int)
initial_position (List[float])
type (CrazyflieType)
tracked (bool)
Safeflie class
- class crazyflies.safeflie.Safeflie(node, id, channel, initialPosition, type, tracked=False)
Bases:
CrazyflieA safe wrapper around the Crazyflie class which ensures that commands are safe to execute on real harware.
- Parameters:
node (rclpy.node.Node)
id (int)
channel (int)
initialPosition (List[float])
type (CrazyflieType)
tracked (bool)